RAAS can be divided into 2 parts:
- plasmatic endocrine cascade
- local tissue RAAS- affecting heart , vessels, adrenal gland and brain)
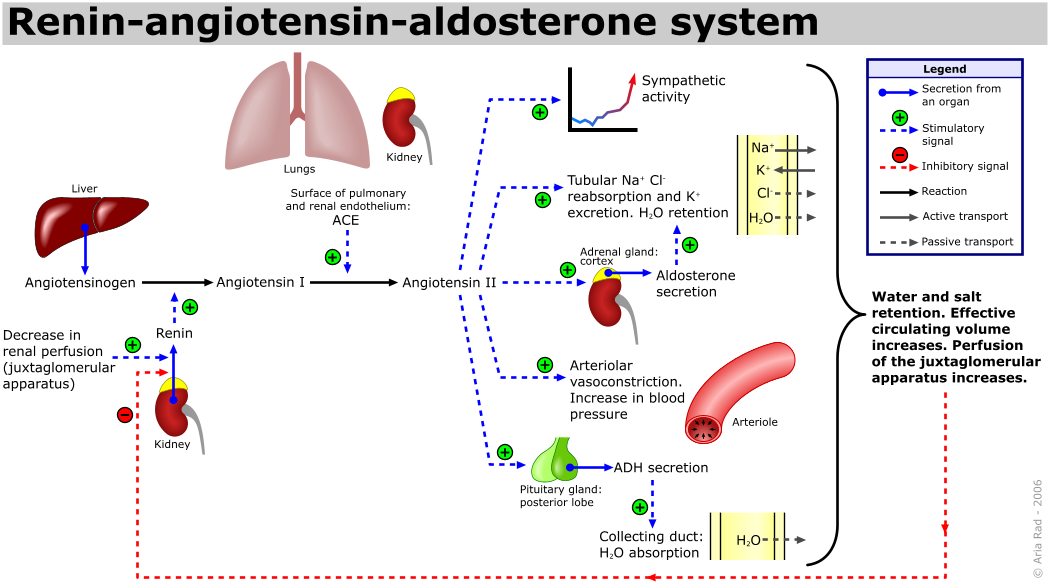
- when blood pressure drop in vas afferens
- drop in sodium ion concentration detected by macula densa in distal tubule.
- when increased in sympathetic activity(when noradrenaline and adrenaline bind to B1 receptor)
AT1 only have small to none its own physiological effect because AT-1 will be converted to AT-2 by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). ACE also responsible for bradykinin breakdown( bradykinin has vasodilator effect), ACE maily bound to endothelial membrane especially in pulmonary circulation.AT -2 has very shot half life , maximum inly 1 minute, because hydrolyzed by plasmatic peptidases. AT -2 has certain effect:
- cause vasoconstriction- increase peripheral vascular resistance.
- increase aldosterone secretion- cause sodium ion retention which lead to water retention
- tissue remodelling in vascular smooth muscle , fibroblast activation, collagen synthesis and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis.
- effect central nervous system by activate thirst center activation, increased sympathetic tonus and ADH and ACTH secretion.
hence if activation of RAAS system occur in chronic condition it can lead to many problem for example:
- atherosclerosis
- vascular hypertrophy
- left ventricle hypertrophy fibrosis
- decrease glomerular filtration rate
- protienuria
- sodium retention
this will lead to hypertension, that can lead to stroke, heart failure and renal failure finally lead to death.

