Proximal convulated tubule(PCT)
-
Approximately 120ml/min of glomerular filtrate
are generated in glomerulus.
-
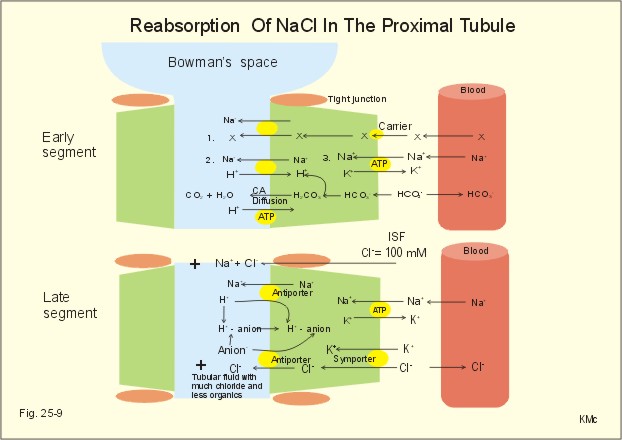
In the PCTmost
of the filtered load reabsorb again which are water by osmotic activity
(80%) most of the Na and under normal condition almost all K+ by passive
diffusion(driven by the positive tubule
electrical potential present along the S2 and S3 segments and by paracellular
solvent drag and glucose actively co transpot with Na from the tubular fluid. Also have Na-H antiporter.
-
Number of substances also secreted by into
tubular fluid for example creatinine, histamine many drugs and toxic.
Loop of Henle

-
Normally about 30ml/min of isotonic filtrate is
delivered to loop oh Henle where counter multiplier mechanism can achieves
concentration of the urine.
-
Loop of Henle important to make sure osmotic
gradient for facultative water reabsorption from collecting tubule to prevent water
loss by kidney. Along the descending limb of the loop of Henle, K is secreted
into the tubule lumen from the interstitium. Along the thick ascending limb, K
is reabsorbed via Na-K-2 Cl cotransport. In the loop, there is net K
reabsorption of 25% of the filtered K. Na reabsorption is controlled by
sympathetic system and aldosterone.
Distal convulated tubule(DCT)
-
In the dist al convulated tubules there are
facultative N and Ca reabsorption and K and P excretion controlled by
aldosterone and parathyroid hormone.
al convulated tubules there are
facultative N and Ca reabsorption and K and P excretion controlled by
aldosterone and parathyroid hormone.
 al convulated tubules there are
facultative N and Ca reabsorption and K and P excretion controlled by
aldosterone and parathyroid hormone.
al convulated tubules there are
facultative N and Ca reabsorption and K and P excretion controlled by
aldosterone and parathyroid hormone.
Collecting duct

-
It contain 2 types of cells: principal cell and
intercalated cell.
-
The principal cell mediates the collecting
duct's influence on sodium and potassium balance via sodium channels and
potassium channels located on the cell's apical membrane. Aldosterone
determines expression of sodium channels with increased aldosterone causing increased
expression of luminal sodium channels. Aldosterone increases the number of
Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase pumps that allow increased
sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion. Vasopressin determines the
expression of aquaporin channels on the cell surface. Together, aldosterone and
vasopressin let the principal cell control the quantity of water that is
reabsorbed.
-
Intercalated cells come in α and β varieties and
participate in acid-base homeostasis
|
Type of cell
|
Secretes
|
Reabsorbs
|
|
α-intercalated
cells
|
acid (via an apical
H+-ATPase and H+/K+ exchanger) in the form ofhydrogen ions
|
bicarbonate (via
band 3, a basolat-eral Cl-/HCO3-exchanger)[5]
|
|
β-intercalated
cells
|
bicarbonate (via
pendrin a specialised api-cal Cl-/HCO3-)
|
acid (via a basal
H+-ATPase)
|
For their contribution to acid-base
homeostasis, the intercalated cells play important roles in the kid-ney's
response to acidosis and alkalosis.
No comments:
Post a Comment