here are complications of diabetes mellitus:
Diabetic retinopathy
Damage of of pericyte covering endothelium causing weakening
of blood vessels and cause microaneurysm and increase permeability resulting in
protein and lipid leakage
Hyperglycemia also increase proliferative processes cause
formation of abnormal vessels resulting in haemorrhage and finally cause visual
problems up to blindness.
Diabetic nephropathy
Complication of diabetes mellitus :
- Non nephrotic
proteinuria(microalbuminemia)
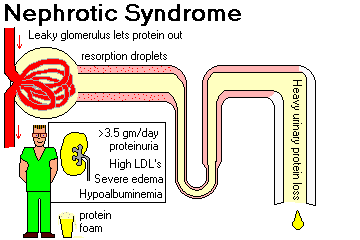
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Renal failure
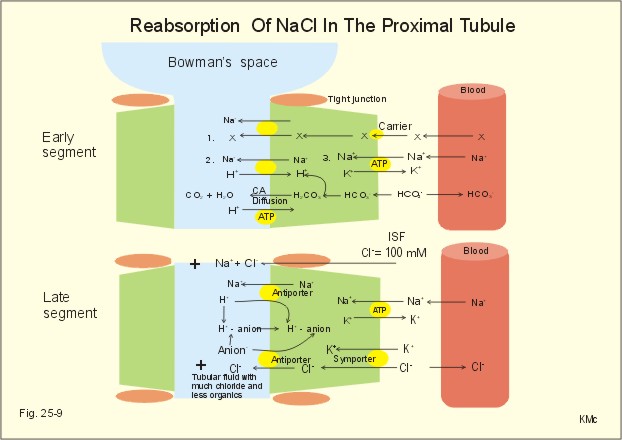
Proteinuria:
Formation of microalbuminemia results fromm loss of negative
charge of basement membrane in glomeruli because AGE(advance glycated
endproduct) decrease of heparin sulphate(negative charge)
Nephrotic syndrome:
Which is loss of negative charge and increase of basement
membrane pore size due to :
1.
Increase of intraglomerular pressure because of
glycosuria, increase glomerular filtration rate and cause hyperfiltration
2.
Imbalance between several growth factors
3.
Non enzymatic glycation of basement membrane
constituents
Chronic renal insufficiency:
Diabetes mellitus causing deposition of glucose to
extracellular space causing thickening of basement membrane and diffuse
proliferation of mesangial cells eventually nodular deposition of hyaline to
mesangium.
Gradually mesangial cells infringe on capillary lumen casue
decrease glomerular filtration up to complete obliteration result in renal
insufficiency.
Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetes mellitus effect nervous system in our bodies.
It cause microangiopathy of small artery that supply nerve
fibers. This is because hyperglycemia .
It also cause distal neuropathy where it cause symmetric loss
of skin sensitivity resulting in diabetic foot and motor problems.
DM also cause wegetative nerve dysfunction :
1.
Impotention and urine incontenetia
2.
Stomach dystonia and diarhoeas
3.
Anhidrosis(can not sweat properly) or profuse
sweating
Macroangiopathy
A disease of the large blood vessels in which fat and blood clots
build up and stick to the vessel walls, blocking the flow of blood. Types of
macroangiopathy include coronary artery disease (macroangiopathy in the heart),
cerebrovascular disease (macroangiopathy in the brain), and peripheral vascular
disease (macroangiopathy that affects, for example, vessels in the legs).when
formation of artherosclerosis increases, this cause arterial hypertension,
coronary heart disease, infarctions, decrease perfusion of the legs result in
ischemic changes and neuropathy finally diabetic foot with ulceration and
formation of gangrene(black foot)
DM accelerated atherosclerosis by formation of:
- Advanced glycated end products(AGE)
- Dyslipoproteinemia-increase VLDL,
cholesterol,LDL, and decrease HDL
AGE:
Formation of AGE is non receptor mediated mechanisms which
effect extracellular matrix especially collagen cross linking. Its also
enhanced synthesis of extracellular matrix components, trapping of LDJ in the
subendothelium and this cause quenches nitric oxide.
Hyperglycemia also modified lipoprotein by glycosylation. Glycosylated
LDL has lower recognition by cellular LDL receptor and cause high concentration
of LDL in blood and increase susceptibility of LDL to oxidative modification
Its also cause endothelial dysfunction by increasing
permeability of endothelial cell monolayers, procoagulant activity, expression
of adhesion molecules and intracellular oxidative stress.
Dyslipoproteinemia:
DM type 1
When there is lack of insulin, reduced inactivation of
lipoprotein lipase and increased activity of hormone sensitive lipase causing
hyperlipoproyeinemia resulting rapid formation of artherosclerosis.
DM type 2
Concentration of insulin normal at the beginning , when
there are certain factor that cause insulin resistance for example
inflammation, hyperglycemia or increased free fatty acids in blood, this cause
muscle and adipose tissue decrease uptake of glucose resulting in
hyperglycemia. When high glucose in blood, this glucose must be converted to
glycogen in liver, but when the capacity of liver to store glycogen reached maximum,
liver must convert glucose tto lipoproteinemia resulting in
hyperlipoproteinemia. Hyperlipoproteinemia increase activity of lipoprotein
lipase and decrease activity of hormone sensitive lipase resulting in fat depositon causing obesity. Hyperlipoproteinemia also increase formation of
artherosclerosis.